Women’s Health: Common Disorders, Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Women’s health encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions that affect physical, mental, and reproductive well-being. Understanding common health disorders, their underlying causes, available treatments, and preventive measures is crucial for empowering women to take charge of their health. This guide delves into prevalent women’s health issues, offering insights into managing and preventing these conditions effectively.
Common Women’s Health Disorders
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death among women globally. Factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to its development. Women often experience different symptoms than men, including nausea, shortness of breath, and back or jaw pain.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Regular cardiovascular screenings
- Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Managing stress effectively
- Medications as prescribed by healthcare providers
2. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Risk factors include age, family history, genetic mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2), and lifestyle choices.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Regular self-examinations and mammograms
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Treatment options: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy.
3. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle, increasing fracture risk. Postmenopausal women are particularly susceptible due to decreased estrogen levels.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation
- Weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises
- Medications like bisphosphonates
- Lifestyle modifications to prevent falls
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts. Symptoms include irregular periods, acne, weight gain, and infertility.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes: balanced diet and regular exercise
- Medications to regulate menstrual cycles and manage symptoms
- Fertility treatments if pregnancy is desired.
5. Depression and Anxiety
Women are more likely than men to experience depression and anxiety due to hormonal fluctuations, life experiences, and societal pressures.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Therapy and counseling
- Medications like antidepressants
- Stress management techniques: mindfulness, yoga, and meditation
- Strong social support networks.
6. Reproductive Health Issues
Conditions such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and cervical cancer significantly impact women’s reproductive health.
Prevention & Treatment:
- Regular gynecological exams and Pap smears
- HPV vaccination to prevent cervical cancer
- Medications and surgical options for endometriosis and fibroids.
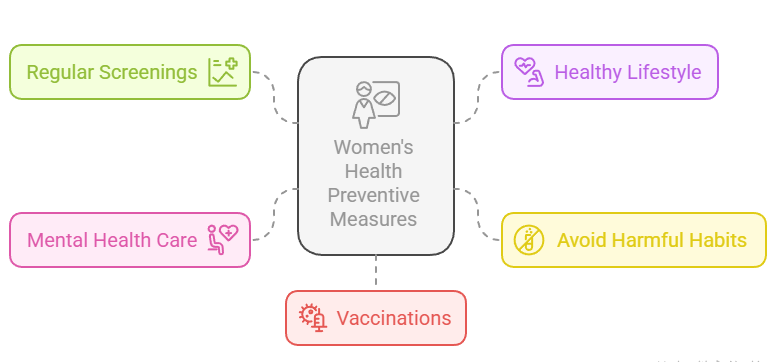
Preventive Measures for Women’s Health
- Regular Screenings: Early detection through mammograms, Pap smears, bone density tests, and cholesterol checks.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Limiting alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and avoiding illicit drugs.
- Mental Health Care: Seeking help for emotional issues and maintaining social connections.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with vaccines like HPV, flu, and hepatitis.
FAQs
Q1: What are the early signs of heart disease in women?
A: Symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, and chest discomfort.
Q2: How often should women get screened for breast cancer?
A: Women aged 40 and above should have annual mammograms, but recommendations may vary based on individual risk factors.
Q3: Can lifestyle changes help manage PCOS?
A: Yes, weight loss, balanced diet, and regular exercise can significantly improve PCOS symptoms.
Q4: What steps can women take to prevent osteoporosis?
A: Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol.
Q5: When should women seek help for mental health issues?
A: If experiencing persistent sadness, anxiety, or loss of interest in activities, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Women’s health is multifaceted, encompassing physical, mental, and reproductive well-being. By understanding common health disorders, recognizing early signs, and adopting preventive measures, women can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Regular consultations with healthcare providers and staying informed are key components of proactive health management.