Tremors & Neurological Disorders: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Tremors & Neurological Disorders , including Kampavata, are interconnected conditions that affect the nervous system, leading to involuntary movements and various neurological symptoms. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life.
Understanding Tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, rhythmic muscle contraction resulting in shaking movements in one or more parts of the body. While tremors can occur in healthy individuals, they are often associated with neurological disorders. In Ayurveda, this condition is commonly referred to under the broader category of Tremors & Neurological Disorders, which are linked to an imbalance in the Vata dosha affecting the nervous system.
Types of Tremors
- Essential Tremor: A common movement disorder causing rhythmic shaking, primarily in the hands, but can also affect the head, voice, and legs.
- Parkinsonian Tremor: Associated with Parkinson’s disease, this tremor typically occurs at rest and may involve the hands, legs, or chin.
- Cerebellar Tremor: Caused by damage to the cerebellum, leading to slow, broad tremors during purposeful movement.
- Dystonic Tremor: Occurs in individuals with dystonia, a movement disorder causing involuntary muscle contractions.
- Psychogenic Tremor: Linked to psychological factors, often characterized by sudden onset and variability in tremor characteristics.

Common Neurological Disorders Associated with Tremors
1. Parkinson’s Disease
Kampavata is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability.
2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the protective sheath (myelin) covering nerve fibers, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. Tremors, known in Ayurveda as Kampavata, can be a symptom of MS.
3. Stroke
An interruption of blood supply to the brain, causing brain cells to die, can lead to various complications. Post-stroke tremors, known in Ayurveda as Kampavata, may occur depending on the area of the brain affected.
4. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Injuries to the brain from external mechanical force can trigger Kampavata, leading to tremors, muscle stiffness, and other neurological symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history can increase the risk of certain Tremors & Neurological Disorders.
- Age: The risk of developing tremors and neurological disorders increases with age.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins and certain medications can contribute to the development of tremors
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like hyperthyroidism, liver failure, and anxiety can cause Tremors & Neurological Disorders.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Involuntary shaking of hands, head, or other body parts.
- Difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Muscle stiffness or rigidity.
- Slurred speech.
- Changes in handwriting
- Fatigue and muscle weakness.
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and diagnosis.
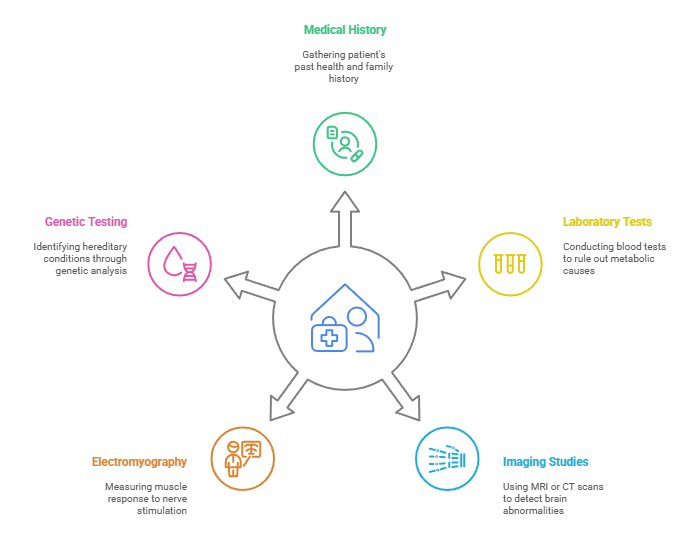
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Tremors & Neurological Disorders involves a comprehensive evaluation, often integrating traditional concepts with modern methods.
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessing symptoms, family history, and conducting neurological exams.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to rule out metabolic causes.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to detect structural abnormalities in the brain.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures muscle response to nerve stimulation.
- Genetic Testing: Identifying hereditary conditions.
Treatment Options
Medications
- Beta-Blockers: Propranolol is commonly used to treat essential tremors.
- Anticonvulsants: Primidone can be effective for tremor control.
- Levodopa: Used in Parkinson’s disease to replenish dopamine levels.
Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Improves muscle strength and coordination.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists in adapting daily activities to manage symptoms.
- Speech Therapy: Helps with speech difficulties associated with neurological disorders.
Surgical Interventions
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Implanting electrodes in specific brain areas to regulate abnormal impulses.
- Focused Ultrasound: Non-invasive procedure targeting brain regions causing tremors.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake.
- Stress management techniques.
- Regular exercise.
- Adequate sleep.
Prevention and Management
While not all neurological disorders and tremors, such as Tremors & Neurological Disorders, can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk by promoting overall health and wellness.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Early detection and management of underlying conditions.
- Healthy Diet: Nutrient-rich foods support nervous system health.
- Avoiding Toxins: Limit exposure to harmful substances.
- Mental Health Care: Addressing psychological factors that may contribute to tremors.
FAQs
- Q1: What is the difference between essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease?
A: Essential tremor primarily affects the hands during movement and is not associated with other Tremors & Neurological Disorders symptoms. Parkinson’s disease tremors occur at rest and are accompanied by other symptoms like rigidity and bradykinesia. - Q2: Can stress cause tremors?
A: Yes, stress and anxiety can exacerbate or even cause tremors, known as psychogenic tremors. - Q3: Are tremors hereditary?
A: Essential tremor often runs in families, indicating a genetic component. - Q4: Is there a cure for tremors?
A: While there’s no cure for most tremors, various treatments can help manage symptoms effectively. - Q5: When should I see a doctor about tremors?
A: If tremors are persistent, worsening, or interfering with daily activities, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation.
Conclusion
Tremors & Neurological Disorders, including conditions like Kampavata, encompass a range of issues that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. Early diagnosis, appropriate therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help control symptoms and improve daily functioning. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, seek medical advice promptly.